
About Me
Hello, my name is Paul and I’m a student at Royal Holloway University. I am currently in my third year of Business Management and this is a Digital Portfolio I made for the course of Social Media, Networks, & Business. This portfolio has for aim to reflect and explain my experience in this course through the discussion of concepts of the course and an analysis using Gephi.
I choose this course because as many students I enjoy using social medias on a daily basis which led me to understand the importance of their use in a market more digital than ever. Before making the choice of this course I’ve already made an internship at F. Iniciativas in the marketing department. This experience gave me a closer look to the use of social medias for a company in its marketing but also in its communication. A year ago, I also had an experience linked with social medias, two other students and I started our business of “dropshipping” which consisted of selling t-shirts on our website made with Shopify. The “dropshipping” allows to select products on websites like “Alibaba” and sell them on your own website without having the product. This business required the good use of social medias in advertising and gave me the aim to learn more about their good use in an organization. This course was exactly what I was looking for since I have for objective to pursue my studies in a master related to social medias and marketing. In fact, I consider social medias as one of the most important part of our future and our markets in every sector through the numerous opportunities it brings.
A concept discussion
Internet has been made to allow access to information to everyone but also allowed anyone to publish a content on any platforms. The concept of “fake news” is more known than ever since it became the word of the year 2017. In fact, fake news became more known since it has been recognized for having played a big role in US presidential elections. These “news” are fabricated, doesn’t bring new content and can be made for various purposes. As one of the most impactful type of fake news, propaganda is generally made to manipulate public opinion. As a matter of fact, Donald Trump’s election at the US presidential in 2016 is known for having been supported by the spread of fake news. These fakes news acted like propaganda, proliferating all around social medias and internet via profiles called “bots” made out of stolen identity. These bots are accounts created by “trolls” which are the authors of these fake news. These fake accounts are made to look like real ones, with for only aim to give enough trust to readers leading them to click on the link and read the article. These bots may also be settled for having automatisms regarding their readers, like following them when they use the same hashtag for example.

These fakes news also generally have headlines made to attract readers, exaggerated without necessarily being linked with the content. In the case of the presidential election, it is absurd to imagine that these fakes news could have impacted the public opinion of a so large country, impacting their vote. As Mark Zuckerberg said in November 2016 regarding the potential influence of fake news published on Facebook on the elections: “Personally I think the idea that fake news on Facebook, which is a very small amount of the content, influenced the election in any way – I think is a pretty crazy idea. »(Mark Zuckerberg, CEO of Facebook). In fact, at this scope, with millions of people sharing fake news regarding Donald Trump, with so many people getting information on social medias, these many fakes news have hugely impacted elections after having manipulated public opinion.
As said before, fake news may have different purposes regarding to their author’s motivation, in every type of fake news, these articles are not following the same codes and practices as journalists and medias. Therefore, these articles make it more difficult for readers to find news they can trust. The rapid proliferation of these fake news increases the number of readers which most of the time aren’t able to make the difference with traditional news. One of the most established is to make money from advertisement implanted in these articles. These articles don’t have the same impact as propaganda, because they don’t manipulate public opinion in a specific way. Propaganda has always existed, and the emergence of these fakes news on social medias was predictable but is hard to manage, especially in spotting them.
In fact, with fake accounts like bots spreading these articles all over social platforms and internet, the public opinion and the integrity of these news is targeted which is now recognized as a problem that needs to be solved by states.
People are now using smartphones more than ever and a part of their use is to get news fast, generally through social medias. In fact, social medias play an important role on the proliferation of these fake news because of the people sharing them with friends and followers without knowing their rightness. In fact, in a world more connected than ever, the proliferation of these fakes news may have a huge impact on people’s opinion, in the wrong way. Taking the example of US presidential shows well how these fakes news can act as propaganda, but in the case of bushfires in Australia, many fake news has been shared all among social medias. In the global movement of support around these bushfires, many were made through the sharing of pictures, showing and giving supports to the firefighters. This movement came up so fast all over internet that many fake pictures have been shared by millions of people and medias, showing wrong information of Australia’s bushfires. This example shows well the importance to regulate these fakes news by spotting them and deleting them before proliferation. As said earlier, states are now considering them as a risk and social medias like Facebook or Instagram are already proposing to users to report fake news and suspicious content.
Internet has been made to allow access to information to everyone but also allowed anyone to publish a content on any platforms. The concept of “fake news” is more known than ever since it became the word of the year 2017. In fact, fake news became more known since it has been recognized for having played a big role in US presidential elections. These “news” are fabricated, doesn’t bring new content and can be made for various purposes. As one of the most impactful type of fake news, propaganda is generally made to manipulate public opinion. As a matter of fact, Donald Trump’s election at the US presidential in 2016 is known for having been supported by the spread of fake news. These fakes news acted like propaganda, proliferating all around social medias and internet via profiles called “bots” made out of stolen identity. These bots are accounts created by “trolls” which are the authors of these fake news. These fake accounts are made to look like real ones, with for only aim to give enough trust to readers leading them to click on the link and read the article. These bots may also be settled for having automatisms regarding their readers, like following them when they use the same hashtag for example.
These fakes news also generally have headlines made to attract readers, exaggerated without necessarily being linked with the content. In the case of the presidential election, it is absurd to imagine that these fakes news could have impacted the public opinion of a so large country, impacting their vote. As Mark Zuckerberg said in November 2016 regarding the potential influence of fake news published on Facebook on the elections: “Personally I think the idea that fake news on Facebook, which is a very small amount of the content, influenced the election in any way – I think is a pretty crazy idea. »(Mark Zuckerberg, CEO of Facebook). In fact, at this scope, with millions of people sharing fake news regarding Donald Trump, with so many people getting information on social medias, these many fakes news have hugely impacted elections after having manipulated public opinion.
As said before, fake news may have different purposes regarding to their author’s motivation, in every type of fake news, these articles are not following the same codes and practices as journalists and medias. Therefore, these articles make it more difficult for readers to find news they can trust. The rapid proliferation of these fake news increases the number of readers which most of the time aren’t able to make the difference with traditional news. One of the most established is to make money from advertisement implanted in these articles. These articles don’t have the same impact as propaganda, because they don’t manipulate public opinion in a specific way. Propaganda has always existed, and the emergence of these fakes news on social medias was predictable but is hard to manage, especially in spotting them.
In fact, with fake accounts like bots spreading these articles all over social platforms and internet, the public opinion and the integrity of these news is targeted which is now recognized as a problem that needs to be solved by states.
People are now using smartphones more than ever and a part of their use is to get news fast, generally through social medias. In fact, social medias play an important role on the proliferation of these fake news because of the people sharing them with friends and followers without knowing their rightness. In fact, in a world more connected than ever, the proliferation of these fakes news may have a huge impact on people’s opinion, in the wrong way. Taking the example of US presidential shows well how these fakes news can act as propaganda, but in the case of bushfires in Australia, many fake news has been shared all among social medias. In the global movement of support around these bushfires, many were made through the sharing of pictures, showing and giving supports to the firefighters. This movement came up so fast all over internet that many fake pictures have been shared by millions of people and medias, showing wrong information of Australia’s bushfires. This example shows well the importance to regulate these fakes news by spotting them and deleting them before proliferation. As said earlier, states are now considering them as a risk and social medias like Facebook or Instagram are already proposing to users to report fake news and suspicious content.

Figure 1. The Fake News Triangle
Furthermore, a research conducted by the Sorbonne University in 2016 have shown that many viral fake news had the same type of titles with high-arousal emotions, bringing joy or fear to attract readers. Another research conducted by the University of Michigan and the University of Vienna came to the conclusion that the proliferation of fake news regarding political movements were more likely to appear in small networks, with the same beliefs facilitating the spread of these news. This discussion about “fake news” led us to understand their impact on public opinion in different moments such as elections time. These false narratives had to appear with the development of internet and are now common on social platforms. These fakes news should be more spotted and reported in order to limit their proliferation.
Social Network Analysis with Gephi
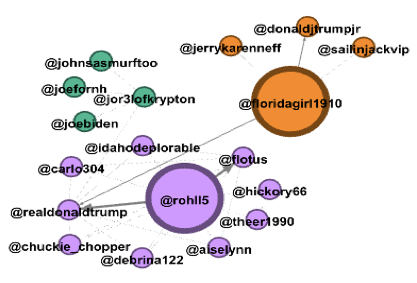
Figure 2. Gephi Analysis of #Donaldtrump

Figure 3. Larger view of the different clusters

Figure 4. Closer look at Hillary Clinton’s network
Above, we can see the social network analysis (SNA) of #donaldtrump made with Gephi. This analysis gives us a closer look of the people having tweeted with this hashtag. This platform allows to have a better view of the relationships between people and how a group is connected and structured. In the case of #donaldtrump we can distinguish different clusters (blue, orange, green and purple) that represent different groups, each tweeting about Donald Trump. The blue nodes are for example composed of Hillary Clinton, the modularity of her node with edges to other blue nodes shows well the political community around her on Twitter; the fact of not seeing edges with the purple nodes can be explained through their political party oppositions. The density of edges and the closeness centrality between Donald Trump and other blue nodes shows well the relationship between these people. In fact, this analysis has for aim to focus on relations between people rather than their attributes, allowing to spot the subgroups and the most influential persons. In this SNA, the different clusters could be understood by visualizing all the different groups with various political opinions, that are not linked and doesn’t have links with each other.
Reflection of learning experience
This course was for me perfectly suited as it deals with Social Medias which are more important than ever before. In this course, I didn’t know about many subjects that were for me still unclear. In fact, nowadays social media have a constant big influence on our world and how we communicate between each other. The world is more and more connected and this allowed the emergence of many opportunities for businesses. In fact, the “datafication” which consists of turning every aspect of our personality on social medias in data that is collected and arranged in order to create value out of it, was for me really interesting since I didn’t know much about it. Through datafication, big organization like Facebook have been able to collect data representing our lives with as many criteria as possible. This led to the collection of our activity on phones and social platforms, giving a better targeting to adds we receive. This concept of “datafication” is directly linked with “filter bubble” which consists of algorithm that personalise people’s feed of information regarding to the websites they clicked on. These bubbles are a threat for democracy and opinions variance by limiting the variety of information given to people, showing them what they like and hiding what they don’t. This module also gave me a closer look to how social medias are useful for businesses by the use of data and to understand why I always find adds of brands that I’ve looked few minutes before, on my Facebook feed for instance. This is one of the thing I didn’t understand when using my phone and social medias that I can now better interpret. The “fake news” I talked about, is something I face every day on my Facebook feed, which I used to consider as non-trusted sources by their suspicious headlines, that I can now spot and report when facing them. One of the important thing of this course was for me the notions of digital marketing in evaluating and planning a marketing campaign on social medias. The first assignment was for me the opportunity to analyse the marketing campaign of a large organization through the understanding of engagement rates and like/click. The return on investment (ROI) of digital marketing campaign can be measured with the analysis of these rates but can also be in the measurement of a profile popularity. The many different social platforms are different and bring different opportunities to the businesses who use them. In fact, Youtube, Facebook, Twitter or Instagram are providing different services to their users with different content used in different ways. On the other side these tools are useful in the internal field of an organization, facilitating exchanges between employees. Among each lecture, I discovered subjects that I may have heard about that I can now understand and talk about. This course helped me in understanding the good use of social platforms at an organizational level which is for me primordial and gave me the knowledge I wanted to acquire when choosing this module.
References
– Derek Greene. (2017). Practical Social Network Analysis with Gephi.Available: http://derekgreene.com/slides/derekgreene_gephi_slides.pdf. Last accessed 4th of January.
– James Carson. (2019). Fake news: What exactly is it – and how can you spot it? Available: https://www.telegraph.co.uk/technology/0/fake-news-exactly-has-really-had-influence/. Last accessed 4th of January.
– Andrew Hutchinson. (2020). What if Fake News Isn’t the Real Problem on Social Media? Available: https://www.socialmediatoday.com/news/what-if-fake-news-isnt-the-real-problem-on-social-media/569711/. Last accessed 3rd of January.
– Margaret Van Heekeren. (2019). The Curative Effect of Social Media on Fake News: A Historical Re-evaluation. Available: https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/1461670X.2019.1642136?src=recsys&journalCode=rjos20. Last accessed 4th of January.
Abonnez-vous à mon blog
Recevez directement le nouveau contenu dans votre boîte de réception.